Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL CHECK constraint to ensure that values stored in a column or group of columns satisfy a Boolean expression.
MySQL 8.0.16 implemented the SQL check constraint. If you use MySQL with the earlier versions, you can emulate a CHECK constraint using a view WITH CHECK OPTION or a trigger.
Introduction to the MySQL CHECK constraint
Before MySQL 8.0.16, the CREATE TABLE allows you to include a table CHECK constraint. However, MySQL ignores all the CHECK constraints:
CHECK(expression)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)As of MySQL 8.0.16, the CREATE TABLE supported essential features of table and column CHECK constraints for all storage engines.
Here is the basic syntax:
CONSTRAINT constraint_name
CHECK (expression)
[ENFORCED | NOT ENFORCED]Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
First, specify the name for the check constraint that you want to create after the CONSTRAINT keyword. If you omit the constraint name, MySQL automatically generates a name with the following convention:
table_name_chk_nCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this convention, n is an ordinal number such as 1,2, and 3. For example, the automatically generated names of CHECK constraints of the parts table will be parts_chk_1, parts_chk_2, and so on.
Second, specify a Boolean expression which must be evaluated to TRUE or UNKNOWN for each row of the table inside the parentheses after the CHECK keyword.
If the expression evaluates to FALSE, the values violate the constraint or a constraint violation occurs.
Note that MySQL treats 1 as true and 0 as false.
Third, optionally specify the enforcement clause to indicate whether the check constraint is enforced:
- Use
ENFORCEDor omit theENFORCEDclause to create and enforce the constraint. - Use
NOT ENFORCEDto create the constraint but not enforce it.
As mentioned earlier, you can define a CHECK constraint as a table constraint or column constraint.
A table CHECK constraint can reference multiple columns whereas the column CHECK constraint can refer to the only column where it is defined.
MySQL CHECK constraint examples
Let’s take some examples of using the CHECK constraints.
1) Creating CHECK constraints as column constraints
The following CREATE TABLE statement creates a new table called parts:
CREATE TABLE parts (
part_no VARCHAR(18) PRIMARY KEY,
description VARCHAR(40),
cost DECIMAL(10,2 ) NOT NULL CHECK (cost >= 0),
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL CHECK (price >= 0)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The parts table has two column CHECK constraints: one for the cost column and the other for the price column.
Because we did not explicitly specify the names of the CHECK constraints, MySQL automatically generated names for them.
To view the table definition with the CHECK constraint name, you use the SHOW CREATE TABLE statement:
SHOW CREATE TABLE parts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
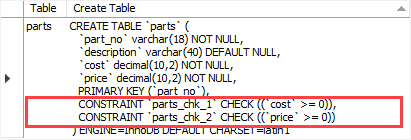
The output indicates that MySQL generated the names (parts_chk_1 and parts_chk_2) for the check constraints.
After creating CHECK constraints, if you insert or update a value that causes the Boolean expression to be false, MySQL rejects the change and issues an error.
This statement inserts a new row into the parts table:
INSERT INTO parts(part_no, description,cost,price)
VALUES('A-001','Cooler',0,-100);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL issued an error:
Error Code: 3819. Check constraint 'parts_chk_2' is violated.Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because the value of the price column is negative which causes the expression price > 0 evaluates to FALSE that results in a constraint violation.
2) Creating CHECK constraints as a table constraints
First, drop the parts table:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS parts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, create a new parts table with one more table CHECK constraint:
CREATE TABLE parts (
part_no VARCHAR(18) PRIMARY KEY,
description VARCHAR(40),
cost DECIMAL(10,2 ) NOT NULL CHECK (cost >= 0),
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL CHECK (price >= 0),
CONSTRAINT parts_chk_price_gt_cost
CHECK(price >= cost)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following new clause defines a table CHECK constraint that ensures the price is always greater than or equal to the cost:
CONSTRAINT parts_chk_price_gt_cost CHECK(price >= cost)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because we explicitly specify the name of the CHECK constraint, MySQL creates the new constraint with the specified name.
Here is the definition of the parts table:
SHOW CREATE TABLE parts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)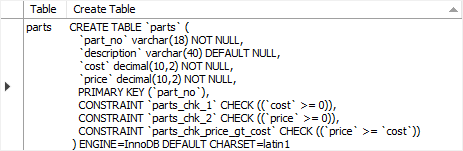
The table CHECK constraint appears at the end of the table definition after the column list.
This statement attempts to insert a new part whose price is less than the cost:
INSERT INTO parts(part_no, description,cost,price)
VALUES('A-001','Cooler',200,100);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the error due to the constraint violation:
Error Code: 3819. Check constraint 'parts_chk_price_gt_cost' is violated.Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Adding a check constraint to a table
To add a check constraint to an existing table, you use the ALTER TABLE ... ADD CHECK statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD CHECK (expression);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you want to explicitly specify the name of the CHECK constraint, you can use the ALTER TABLE ... ADD CONSTRAINT ... CHECK statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD CONSTRAINT contraint_name
CHECK (expression);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statement adds a CHECK constraint to the parts table:
ALTER TABLE parts
ADD CHECK (part_no <> description);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This CHECK constraint prevents you from having the part_no identical to the description.
For example, the following INSERT statement will be rejected:
INSERT INTO parts
VALUES('A','A',100,120);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
ERROR 3819 (HY000): Check constraint 'parts_chk_3' is violated.Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Removing a check constraint from a table
To remove a CHECK constraint from a table, you use the ALTER TABLE ... DROP CHECK statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP CHECK constraint_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statement removes the CHECK constraint parts_chk_3 from the parts table:
ALTER TABLE parts
DROP CHECK parts_chk_3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary
- Use
CHECKconstraints to ensure values stored in a column satisfy a Boolean condition. - Use the
CHECK(expression)to define aCHECKconstraint. - Use the
ALTER TABLE ... ADD CHECKto add aCHECKconstraint to a table. - Use the
ALTER TABLE ... DROP CHECKto remove aCHECKconstraint from a table.