Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the MySQL RANK() function and how to apply it to assign a rank to each row within the partition of a result set.
Note that MySQL has been supporting the RANK() function and other window functions since version 8.0
Introduction to MySQL RANK() function
The RANK() function assigns a rank to each row within the partition of a result set. The rank of a row is specified by one plus the number of ranks that come before it.
The following shows the syntax of the RANK() function:
RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY <expression>[{,<expression>...}]
ORDER BY <expression> [ASC|DESC], [{,<expression>...}]
)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divides the result sets into partitions. TheRANK()function is performed within partitions and re-initialized when crossing the partition boundary. - Second, The
ORDER BYclause sorts the rows within a partition by one or more columns or expressions.
Unlike the ROW_NUMBER() function, the RANK() function does not always return consecutive integers.
Suppose you have a sample table as follows:
CREATE TABLE t (
val INT
);
INSERT INTO t(val)
VALUES(1),(2),(2),(3),(4),(4),(5);
SELECT * FROM t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement uses the RANK() function to assign a rank to each row from the result set in the t table:
SELECT
val,
RANK() OVER (
ORDER BY val
) my_rank
FROM
t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
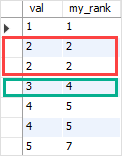
The output indicates that the second and third rows have the same ties so they receive the same rank 2.
The fourth row has rank 4 because the RANK() function skips the rank 3.
MySQL RANK() function example
Let’s use the sales table created in the window function tutorial for the demonstration.
If you have not created the sales table yet, here is the script:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sales(
sales_employee VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
fiscal_year INT NOT NULL,
sale DECIMAL(14,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(sales_employee,fiscal_year)
);
INSERT INTO sales(sales_employee,fiscal_year,sale)
VALUES('Bob',2016,100),
('Bob',2017,150),
('Bob',2018,200),
('Alice',2016,150),
('Alice',2017,100),
('Alice',2018,200),
('John',2016,200),
('John',2017,150),
('John',2018,250);
SELECT * FROM sales;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here’s data of the sales table:
+----------------+-------------+--------+
| sales_employee | fiscal_year | sale |
+----------------+-------------+--------+
| Alice | 2016 | 150.00 |
| Alice | 2017 | 100.00 |
| Alice | 2018 | 200.00 |
| Bob | 2016 | 100.00 |
| Bob | 2017 | 150.00 |
| Bob | 2018 | 200.00 |
| John | 2016 | 200.00 |
| John | 2017 | 150.00 |
| John | 2018 | 250.00 |
+----------------+-------------+--------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following statement uses the RANK() function to rank the sales employees by sales amount every year:
SELECT
sales_employee,
fiscal_year,
sale,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY
fiscal_year
ORDER BY
sale DESC
) sales_rank
FROM
sales;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+----------------+-------------+--------+------------+
| sales_employee | fiscal_year | sale | sales_rank |
+----------------+-------------+--------+------------+
| John | 2016 | 200.00 | 1 |
| Alice | 2016 | 150.00 | 2 |
| Bob | 2016 | 100.00 | 3 |
| Bob | 2017 | 150.00 | 1 |
| John | 2017 | 150.00 | 1 |
| Alice | 2017 | 100.00 | 3 |
| John | 2018 | 250.00 | 1 |
| Alice | 2018 | 200.00 | 2 |
| Bob | 2018 | 200.00 | 2 |
+----------------+-------------+--------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)In this example:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause breaks the result sets into partitions by fiscal year. - Then, the
ORDER BYclause sorts the sales employees by sales in descending order.
MySQL RANK() function with CTE example
The following statement uses the RANK() function to find the top three highest valued orders in each year:
WITH order_values AS(
SELECT
orderNumber,
YEAR(orderDate) order_year,
quantityOrdered*priceEach AS order_value,
RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY YEAR(orderDate)
ORDER BY quantityOrdered*priceEach DESC
) order_value_rank
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN orderdetails USING (orderNumber)
)
SELECT
*
FROM
order_values
WHERE
order_value_rank <=3;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
+-------------+------------+-------------+------------------+
| orderNumber | order_year | order_value | order_value_rank |
+-------------+------------+-------------+------------------+
| 10196 | 2003 | 9571.08 | 1 |
| 10206 | 2003 | 9568.73 | 2 |
| 10201 | 2003 | 9394.28 | 3 |
| 10312 | 2004 | 10286.40 | 1 |
| 10348 | 2004 | 9974.40 | 2 |
| 10304 | 2004 | 9467.68 | 3 |
| 10403 | 2005 | 11503.14 | 1 |
| 10405 | 2005 | 11170.52 | 2 |
| 10407 | 2005 | 10723.60 | 3 |
+-------------+------------+-------------+------------------+
9 rows in set (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)In this example:
- First, use a common table expression (CTE) to get the order number, order year, and rank. To rank orders by order value in each year, we used the
RANK()function that partitioned the rows by order year and sorted the order value in descending order. - Then, select only the orders whose rank is less than or equal to three.
Summary
- Use the MySQL
RANK()function to assign a rank to each row in a result set.