Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the CREATE USER .. ACCOUNT LOCK and ALTER TABLE .. ACCOUNT LOCK statements to lock user accounts in MySQL server.
To lock a user account, you can use the CREATE USER .. ACCOUNT LOCK statement:
CREATE USER account_name
IDENTIFIED BY 'password'
ACCOUNT LOCK;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you omit the ACCOUNT LOCK clause, the CREATE USER statement creates a new user in an unlocked state by default.
Or you can use the ALTER USER .. ACCOUNT LOCK statement to lock an existing user account:
ALTER USER account_name
IDENTIFIED BY 'password'
ACCOUNT LOCK;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL records the account locking state in the account_locked column of the mysql.user system table. The values Y and N for locked and unlocked respectively.
Note that to unlock user accounts, you use the ALTER USER .. ACCOUNT UNLOCK statement.
Locking user account examples
Let’s take some examples of locking user accounts.
1) Using ACCOUNT LOCK to lock a new account example
First, create a new user account david@localhost in the locked state:
CREATE USER david@localhost
IDENTIFIED BY 'Secret!Pass1'
ACCOUNT LOCK;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, show the user account and its status:
SELECT
user, host, account_locked
FROM
mysql.user
WHERE
user = 'david' AND
host='localhost';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)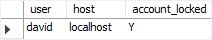
The account_locked column in the mysql.user table indicates whether an account is locked or not, Y for locked and N for not locked.
Third, use the user account david to connect to the MySQL Server, you will receive an error:
mysql -u david -p
Enter password: ************Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the error message:
ERROR 3118 (HY000): Access denied for user 'david'@'localhost'. Account is locked.
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Using ACCOUNT LOCK to lock an existing user account example
First, create a user account dolphin@localhost:
CREATE USER dolphin@localhost
IDENTIFIED BY 'Secret!pass1';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, use the user account dolphin@localhost to login to the MySQL server:
mysql -u dolphin -p
Enter password: ********Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The user account dolphin@localhost can log in successfully.
Third, use the ALTER TABLE LOCK ACCOUNT statement to lock the user account dolphin@localhost:
ALTER USER dolphin@localhost
ACCOUNT LOCK;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Fourth, show the user status:
SELECT
user, host, account_locked
FROM
mysql.user
WHERE
user = 'dolphin';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)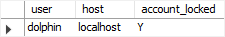
The user account dolphin was locked as expected.
The Locked_connects variables status variable shows the number of attempts to connect to MySQL Server using a locked account.
When a locked account attempts to log in, MySQL increases the Locked_connects status variable by 1.
To display the number of attempts of the locked accounts, you use this command:
SHOW GLOBAL STATUS
LIKE 'Locked_connects';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the CREATE USER .. ACCOUNT LOCK and ALTER TABLE .. ACCOUNT LOCK statements to lock user accounts in the MySQL server.