Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL COUNT() function to return the number of rows in a table.
Introduction to the MySQL COUNT() function
The COUNT() function is an aggregate function that returns the number of rows in a table. The COUNT() function allows you to count all rows or only rows that match a specified condition.
The COUNT() function has three forms:
COUNT(*)COUNT(expression)COUNT(DISTINCT expression)
COUNT(*) function
The COUNT(*) function returns the number of rows in a result set returned by a SELECT statement. The COUNT(*) returns the number of rows including duplicate, non-NULL and NULL rows.
COUNT(expression)
The COUNT(expression) returns the number of rows that do not contain NULL values as the result of the expression.
COUNT(DISTINCT expression)
The COUNT(DISTINCT expression) returns the number of distinct rows that do not contain NULL values as the result of the expression.
The return type of the COUNT() function is BIGINT. The COUNT() function returns 0 if there is no matching row found.
MySQL COUNT() function illustration
Setting up a sample table
First, create a table called count_demos:
CREATE TABLE count_demos (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
val INT
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the count_demos table:
INSERT INTO count_demos(val)
VALUES(1),(1),(2),(2),(NULL),(3),(4),(NULL),(5);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, query data from the count_demos table:
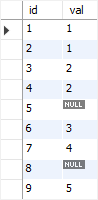
SELECT * FROM count_demos;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL COUNT(*) example
The following statement uses the COUNT(*) function to return all rows from the count_demos table:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM count_demos;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)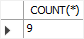
This example uses the COUNT(*) function with a WHERE clause to specify a condition to count only rows whose value in the column val is 2:
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM count_demos
WHERE val = 2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL COUNT(expression) example
If you specify the val column in the COUNT() function, the COUNT() function will count only rows with non-NULL values in the val column:
SELECT COUNT(val)
FROM count_demos;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Notice that two NULL values are not counted.
MySQL COUNT(DISTINCT expression) example
This example uses COUNT(DISTINCT expression) to count non-NULL and distinct values in the column val:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT val)
FROM count_demos;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)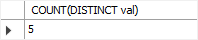
MySQL COUNT() function practical examples
We’ll use the products table from the sample database for the next examples:
1) Using MySQL COUNT(*) function with a GROUP BY example
The COUNT(*) function is often used with a GROUP BY clause to return the number of elements in each group.
For example, this statement uses the COUNT() function with the GROUP BY clause to return the number of products in each product line:
SELECT
productLine,
COUNT(*)
FROM
products
GROUP BY productLine;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)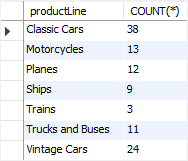
Similarly, this example uses the COUNT(*) function to find the number of products supplied by each vendor:
SELECT
productVendor,
COUNT(*)
FROM
products
GROUP BY productVendor
ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)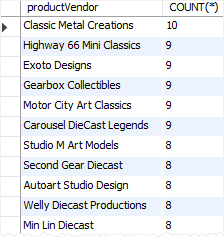
2) Using MySQL COUNT(*) with a HAVING clause example
To find vendors who supply at least 9 products, you use the COUNT(*) function in the HAVING clause as shown in the following query:
SELECT
productVendor,
COUNT(*)
FROM
products
GROUP BY productVendor
HAVING COUNT(*) >= 9
ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)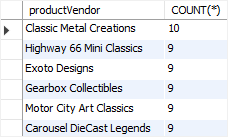
3) MySQL COUNT IF example
You can use a control flow expression and functions e.g., IF, IFNULL, and CASE in the COUNT() function to count rows whose values match a condition.
See the following orders table from the sample database:

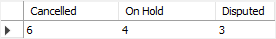
The following query use COUNT() with IF function to find the number of canceled, on hold, and disputed orders from the orders table:
SELECT
COUNT(IF(status = 'Cancelled', 1, NULL)) 'Cancelled',
COUNT(IF(status = 'On Hold', 1, NULL)) 'On Hold',
COUNT(IF(status = 'Disputed', 1, NULL)) 'Disputed'
FROM
orders;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The IF() function returns 1 if the order’s status is canceled, on hold, or disputed, otherwise, it returns NULL.
The COUNT function only counts 1, not NULL values, therefore, the query returns the number of orders based on the corresponding status.
In this tutorial, you have learned various techniques to count the number of rows in a table using the MySQL COUNT function.