Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL BETWEEN operator to determine whether a value is in a range of values.
Introduction to MySQL BETWEEN Operator
The BETWEEN operator is a logical operator that specifies whether a value is in a range or not. Here’s the syntax of the BETWEEN operator:
value BETWEEN low AND high;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The BETWEEN operator returns 1 if:
value >= low AND value <= highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Otherwise, it returns 0.
If the value, low, or high is NULL, the BETWEEN operator returns NULL .
For example, the following statement returns 1 because 15 is between 10 and 20:
SELECT 15 BETWEEN 10 AND 20;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following example returns 0 because 15 is not between 20 and 30:
SELECT 15 BETWEEN 20 AND 30;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that MySQL treats 1 as true and 0 as false.
NOT BETWEEN
To negate the BETWEEN operator, you use the NOT operator:
value NOT BETWEEN low AND highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The NOT BETWEEN operator returns 1 if:
value < low OR value > highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Otherwise, it returns 0.
For example, the following statement returns 0 because 15 is not between 10 and 20 is not true:
SELECT 15 NOT BETWEEN 10 AND 20;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In practice, you’ll use the BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause of the SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.
MySQL BETWEEN operator examples
Let’s practice with some examples of using the BETWEEN operator.
1) Using MySQL BETWEEN with Numbers
See the following products table in the sample database:
The following example uses the BETWEEN operator to find products whose buy prices between 90 and 100:
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
buyPrice
FROM
products
WHERE
buyPrice BETWEEN 90 AND 100;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)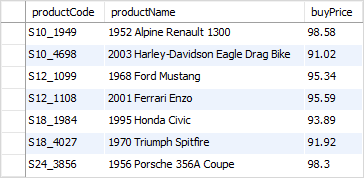
This query uses the greater than or equal (>=) and less than or equal to ( <= ) operators instead of the BETWEEN operator to get the same result:
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
buyPrice
FROM
products
WHERE
buyPrice >= 90 AND buyPrice <= 100;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To find the products whose buy prices are not between $20 and $100, you use the NOT BETWEEN operator as follows:
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
buyPrice
FROM
products
WHERE
buyPrice NOT BETWEEN 20 AND 100;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)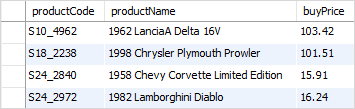
You can rewrite the query above using the less than (<), greater than (>), and the logical operator (AND) like this:
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
buyPrice
FROM
products
WHERE
buyPrice < 20 OR buyPrice > 100;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Using MySQL BETWEEN operator with dates example
See the following orders table:
To check if a value is between a date range, you should explicitly cast the value to the DATE type.
For example, the following statement returns the orders with the required dates between 01/01/2003 to 01/31/2003:
SELECT
orderNumber,
requiredDate,
status
FROM
orders
WHERE
requireddate BETWEEN
CAST('2003-01-01' AS DATE) AND
CAST('2003-01-31' AS DATE);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)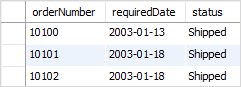
In this example, we use the CAST() to cast the literal string '2003-01-01' into a DATE value:
CAST('2003-01-01' AS DATE)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary
- Use the MySQL
BETWEENoperator to test if a value falls within a range of values.