Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about MySQL collation and how to set character sets and collations for the MySQL server, database, table, and column.
Introduction to MySQL collation
A MySQL collation is a set of rules used to compare characters in a particular character set. Each character set in MySQL has at least one default collation. It can have more than one collation. However, two character sets cannot have the same collation.
MySQL provides the SHOW CHARACTER SET statement that allows you to get the default collations of character sets:
SHOW CHARACTER SET;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)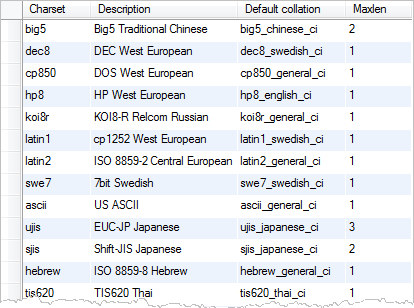
The values of the default collation column specify the default collations for the character sets.
By convention, a collation for a character set begins with the character set name and ends with _ci (case insensitive) _cs (case sensitive) or _bin (binary).
To get all collations for a given character set, you use the SHOW COLLATION statement as follows:
SHOW COLLATION LIKE 'character_set_name%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statement gets all collations for the latin1 character set:
SHOW COLLATION LIKE 'latin1%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)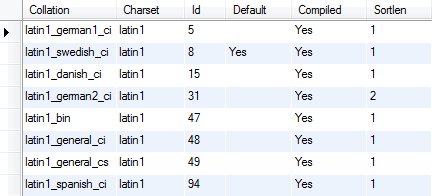
As mentioned above, each character set has a default collation e.g., latin1_swedish_ci is the default collation of the latin1 character set.
Setting character sets and collations
MySQL allows you to specify character sets and collations at four levels:
- Server
- Database
- Table
- Column
1) Setting character sets and collations at the server Level
MySQL uses the latin1 as the default character set. Therefore, the default collation is latin1_swedish_ci. You can change these settings at server startup.
If you specify one character set at server startup, MySQL will use the default collation of that character set. However, if you specify both a character set and a collation explicitly, MySQL will use the character set and collation for all databases that you will create.
The following statement sets the utf8 character set and utf8_unicode_cs collation for the server via the command line:
>mysqld --character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_unicode_csCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Setting character sets and collations at the database level
When you create a database but do not specify the character set and collation, MySQL will use the default character set and collation of the server for the new database.
You can override the default settings at the database level by using CREATE DATABASE statement:
CREATE DATABASE database_name
CHARACTER SET character_set_name
COLLATE collation_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)or using the ALTER DATABASE statement:
ALTER DATABASE database_name
CHARACTER SET character_set_name
COLLATE collation_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL will use the database’s character set and collation by default for the tables that you create in the database.
3) Setting character sets and collations at the table level
A database may contain tables with character sets and collations that are different from the database’s character set and collation.
You can specify the default character set and collation for a table when you create the table by using the CREATE TABLE statement:
CREATE TABLE table_name(
...
)
CHARACTER SET character_set_name
COLLATE collation_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)or when you alter the table using the ALTER TABLE statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name(
...
)
CHARACTER SET character_set_name
COLLATE collation_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)4) Setting character set and collation at column level
A column of type CHAR , VARCHAR or TEXT can have its own character set and collation different from the table’s character set and collation.
The CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statement allows you to override the character set and collation for a specific column:
column_name [CHAR | VARCHAR | TEXT] (length)
CHARACTER SET character_set_name
COLLATE collation_nameCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The rules for setting the character set and collation are:
- If you specify both a character set and a collation explicitly, the character set and collation are used.
- If you specify a character set and omit the collation, the default collation of the character set is used.
- If you specify a collation without a character set, the character set associated with the collation is used.
- If you omit both character set and collation, the default character set and collation are used.
Let’s take a look at some examples of setting the character sets and collations.
Examples of setting character sets and collations
First, create a new database with utf8 as the character set and utf8_unicode_ci as the default collation:
CREATE DATABASE mydb
CHARACTER SET utf8
COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because we specify the character set and collation for the mydb database explicitly, the mydb won’t take the default character set and collation of the database server.
Second, create a new table named t1 in the mydb database:
USE mydb;
CREATE TABLE t1(
c1 char(25)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this CREATE TABLE statement, we don’t specify the character set and collation for the t1 table. Therefore, MySQL will use the character set and collation of the database for the t1 table. In this case, the t1 table will have utf8 as the default character set and utf8_unicode_ci as the default collation.
Third, change the character set and collation of the table t1 to latin1 and latin1_german1_ci:
ALTER TABLE t1
CHARACTER SET latin1
COLLATE latin1_german1_ci;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The c1 column in the t1 table has latin1 as the character set and latin1_german1_ci as the collation.
Finally, change the character set of the c1 column to latin1 :
ALTER TABLE t1
MODIFY c1 VARCHAR(25)
CHARACTER SET latin1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Now, the c1 column has the latin1 character set, but what about its collation? Is it inheriting the latin1_german1_ci collation from the table’s collation?
The answer is no. The reason is that the default collation of the latin1 character set is latin1_swedish_ci, therefore, the c1 column will have the latin1_swedish_ci collation.
In this tutorial, you have learned about MySQL collation and how to specify character sets and collations for the MySQL server, databases, tables, and columns.
Reference
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/charset.html – MySQL character set support
- http://collation-charts.org/mysql60/ – MySQL collation charts