Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn various techniques for exporting a MySQL table to a CSV file.
The CSV stands for comma-separated values. The CSV file format is often used to exchange data between applications such as Microsoft Excel, Open Office, Google Docs, and so on.
Having data from the MySQL database in CSV file format will be useful because you can analyze and format the data in the way you want.
MySQL provides an easy way to export the query’s result into a CSV file that resides on the database server.
1) Exporting a table to a CSV file using SELECT … INTO OUTFILE statement
We’ll illustrate how to export the orders table from the classicmodels sample database into a CSV file located on the MySQL Server.
First, open the Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Unix-like systems and connect to the MySQL server:
mysql -u root -pCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, change the current database to classicmodels:
USE classicmodels;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, show the value of the secure_file_priv variable:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "secure_file_priv";Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)On Windows server, the output is like the following:
+------------------+------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+------------------------------------------------+
| secure_file_priv | C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Uploads\ |
+------------------+------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)On Ubuntu, the output will look like:
+------------------+-----------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+-----------------------+
| secure_file_priv | /var/lib/mysql-files/ |
+------------------+-----------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The secure_file_priv setting indicates the directory where you are allowed to store the output file.
Finally, retrieve data from the orders table and export the result set into the orders.csv file:
SELECT * FROM orders
INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/orders.csv'
FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '"'
TERMINATED BY ','
ESCAPED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Notice that the orders.csv file must not exist in the directory C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/. Otherwise, the statement will issue an error:
ERROR 1086 (HY000): File 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/orders.csv' already existsCode language: JavaScript (javascript)How it works:
First, retrieve data from the orders table:
SELECT * FROM ordersCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, specify the CSV output file (orders.csv) stored in the allowed directory (C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads) in the INTO OUTFILE clause:
INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/orders.csv' Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Notice you have to replace the backslash \ by the forward slash / in the directory on Windows to make it work.
Third, define the format of the output file as CSV by specifying how fields and lines in the output are formatted:
FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '"'
TERMINATED BY ','
ESCAPED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the detail of each option:
- FIELDS ENCLOSED BY ‘”‘: specifies that each field in the output file will be enclosed by double quotation marks (
"). - TERMINATED BY ‘,’: specifies that fields in the output file are separated (terminated) by a comma (
,). - ESCAPED BY ‘”‘: specifies the character used to escape special characters. In this case, it’s a double quotation mark (
"). - LINES TERMINATED BY ‘\r\n’: specifies that each line in the output file is terminated by a carriage return (\r) followed by a newline character (\n), which is a common line-ending sequence in Windows environments.
Here is the excerpt from the orders.csv file:
"10100","2003-01-06","2003-01-13","2003-01-10","Shipped","N,"363"
"10101","2003-01-09","2003-01-18","2003-01-11","Shipped","Check on availability.","128"
"10102","2003-01-10","2003-01-18","2003-01-14","Shipped","N,"181"
...Code language: PHP (php)Adding a timestamp to the CSV output file
You often need to export data into a CSV file whose name contains a timestamp indicating when the file is created. To achieve this, you need to use a MySQL prepared statement.
The following commands export the entire orders table into a CSV file with a timestamp as a part of the file name:
set @ts = DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'_%Y_%m_%d_%H_%i_%s');
set @filename = concat(replace(@@secure_file_priv,'\\','/'), 'orders', @ts, '.csv');
select @filename;
set @cmd = CONCAT("SELECT * FROM orders INTO OUTFILE '",
@filename,
"' FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '\"' TERMINATED BY ',' ESCAPED BY '\"'",
" LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';");
prepare statement from @cmd;
execute statement;
deallocate prepare statement;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In these statements:
- First, construct a query with the current timestamp as a part of the file name.
- Second, prepare the statement for execution by using a
PREPAREstatement. - Third, execute the statement by using the
EXECUTEcommand.
Creating a stored procedure that exports a query result into a CSV file
To simplify the process of exporting the result set of a query into a CSV file, we can create a stored procedure that generates a CSV file from a query’s result set:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE ExportToCSV(
IN query_text TEXT,
IN filename VARCHAR(255)
)
BEGIN
DECLARE ts VARCHAR(20);
DECLARE cmd VARCHAR(1000);
-- Construct the full file name
SET filename = CONCAT(REPLACE(@@secure_file_priv, '\\', '/'), filename);
-- Construct the SQL command
SET @cmd = CONCAT(
query_text,
" INTO OUTFILE '", filename,
"' FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '\"' TERMINATED BY ',' ESCAPED BY '\"'",
" LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';"
);
-- Prepare and execute the statement
PREPARE statement FROM @cmd;
EXECUTE statement;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE statement;
SELECT filename;
END //
DELIMITER ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, you can export the employees table to employees.csv file as follows:
CALL ExportToCSV(
'select * from employees',
'employees.csv'
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| filename |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/employees.csv |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)You can retrieve the CSV file in the output: C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/employees.csv
Adding column heading to the CSV output file
It would be convenient if the CSV file contains the first line as the column headings so that the file is more understandable.
To add the column headings, you can use a UNION operator as follows:
SELECT 'Order no', 'Order date', 'Required Date', 'Shipped Date', 'Status', 'Comments', 'Customer No'
UNION
SELECT * FROM orders
INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/orders_heading.csv'
FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '"'
TERMINATED BY ','
ESCAPED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Mapping NULL to other values
If the values in the result set contain NULL values, the target file will contain "N instead of NULL.
To fix this issue, you need to replace the NULL value by another value, for example, not available ( N/A ) by using the IFNULL function as shown in the following query:
SELECT 'Order no', 'Order date', 'Required Date', 'Shipped Date', 'Status', 'Comments', 'Customer No'
UNION
SELECT orderNumber, orderDate, requiredDate, IFNULL(shippedDate,"N/A"), status, IFNULL(comments, "N/A"), customerNumber
FROM orders
INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/orders_full.csv'
FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '"'
TERMINATED BY ','
ESCAPED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In the SELECT clause, we replace NULL in the shippedDate and comments columns with the string "N/A".
2) Exporting data to CSV file using MySQL Workbench
If you don’t have access to the MySQL server to retrieve the exported CSV file, you can use MySQL Workbench to export the result set of a query to a CSV file in your local computer as follows:
- First, execute a query to get its result set.
- Second, from the result panel, click “export recordset to an external file”. Note that a result set is also known as a recordset.
- Third, a new dialog is displayed and asks you for a filename and file format. Enter the file name, choose CSV as the file format, and click the Save button.
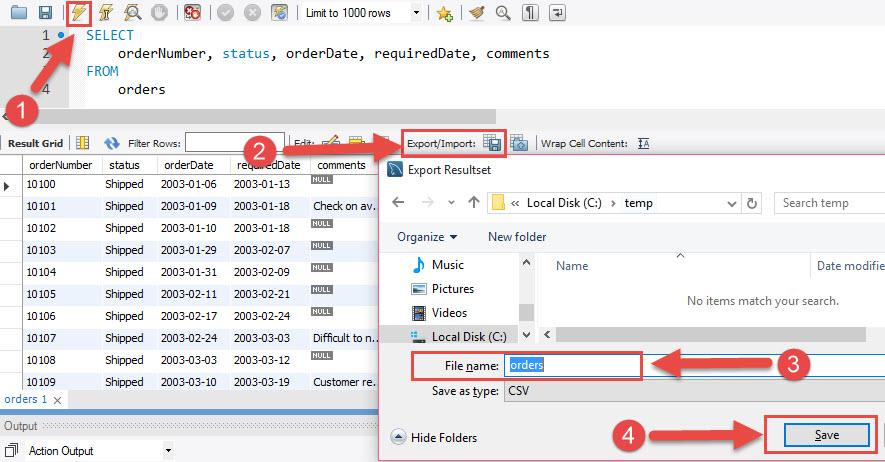
The CSV file exported by MySQL Workbench supports column headings, NULL values and other features.
Summary
- Use the
SELECT ... INTO OUTFILEstatement to export a table to a CSV file on the MySQL Server. - Use MySQL Workbench to export a table to a CSV file on your local computer.