Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL interval values to perform date and time arithmetic.
Introduction to MySQL interval values
MySQL interval values are used mainly for date and time calculations. To create an interval value, you use the following expression:
INTERVAL expr unitCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Followed by the INTERVAL keyword is the expr that determines the interval value, and unit that specifies the interval unit. For example, to create a 1-day interval, you use the following expression:
INTERVAL 1 DAYCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Notice that the INTERVAL and UNIT are case-insensitive therefore the following expression is equivalent to the one above:
interval 1 dayCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We mainly use interval values for date and time arithmetic as shown below:
date + INTERVAL expr unit
date - INTERVAL expr unitCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The interval values are also used in various temporal functions such as DATE_ADD,DATE_SUB, TIMESTAMPADD and TIMESTAMPDIFF.
MySQL defines standard formats for expr and unit as illustrated in the following table:
| unit | expr |
|---|---|
| DAY | DAYS |
| DAY_HOUR | ‘DAYS HOURS’ |
| DAY_MICROSECOND | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| DAY_MINUTE | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES’ |
| DAY_SECOND | ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| HOUR | HOURS |
| HOUR_MICROSECOND | ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| HOUR_MINUTE | ‘HOURS:MINUTES’ |
| HOUR_SECOND | ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| MICROSECOND | MICROSECONDS |
| MINUTE | MINUTES |
| MINUTE_MICROSECOND | ‘MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| MINUTE_SECOND | ‘MINUTES:SECONDS’ |
| MONTH | MONTHS |
| QUARTER | QUARTERS |
| SECOND | SECONDS |
| SECOND_MICROSECOND | ‘SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’ |
| WEEK | WEEKS |
| YEAR | YEARS |
| YEAR_MONTH | ‘YEARS-MONTHS’ |
MySQL interval examples
The following statement adds 1 day to January 1st 2020 that returns January 2nd 2020:
SELECT '2020-01-01' + INTERVAL 1 DAY;
+-------------------------------+
| '2020-01-01' + INTERVAL 1 DAY |
+-------------------------------+
| 2020-01-02 |
+-------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If an interval value is used in an expression that involves a DATE or DATETIME value and the interval value is on the right side of the expression, you can use the negative value of the expr as shown in the following example:
SELECT '2020-01-01' + INTERVAL -1 DAY;
+--------------------------------+
| '2020-01-01' + INTERVAL -1 DAY |
+--------------------------------+
| 2019-12-31 |
+--------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement shows how to use DATE_ADD and DATE_SUB to add/subtract 1 month to/from a date value:
SELECT DATE_ADD('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 MONTH) 1_MONTH_LATER,
DATE_SUB('2020-01-01',INTERVAL 1 MONTH) 1_MONTH_BEFORE;
+---------------+----------------+
| 1_MONTH_LATER | 1_MONTH_BEFORE |
+---------------+----------------+
| 2020-02-01 | 2019-12-01 |
+---------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following query uses TIMESTAMPADD(unit,interval,expression) function to add 30 minutes to a timestamp value:
SELECT TIMESTAMPADD(MINUTE,30,'2020-01-01') 30_MINUTES_LATER;
+---------------------+
| 30_MINUTES_LATER |
+---------------------+
| 2020-01-01 00:30:00 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL interval practical example
Let’s create a new table called memberships for demonstration:
CREATE TABLE memberships (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(355) NOT NULL,
plan VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
expired_date DATE NOT NULL
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In the memberships table, the expired_date column stores the membership’s expiration date for each member.
The following statement inserts some rows into the memberships table.
INSERT INTO memberships(email, plan, expired_date)
VALUES('[email protected]','Gold','2017-07-13'),
('[email protected]','Platinum','2017-07-10'),
('[email protected]','Silver','2017-07-15'),
('[email protected]','Gold','2017-07-20'),
('[email protected]','Silver','2017-07-08');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Suppose today is 2017-07-06, you can find the members whose memberships expired within 7 days using the following query:
SELECT
email,
plan,
expired_date,
DATEDIFF(expired_date, '2017-07-06') remaining_days
FROM
memberships
WHERE
'2017-07-06' BETWEEN DATE_SUB(expired_date, INTERVAL 7 DAY) AND expired_date;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)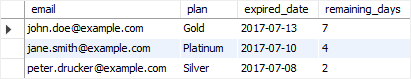
In this query, we used the DATE_SUB function to subtract the expired date by 7 days specified by an interval value (INTERVAL 7 DAY).
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use MySQL interval value for the date and time arithmetic.