Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL LIKE operator to query data based on a specified pattern.
Introduction to MySQL LIKE operator
The LIKE operator is a logical operator that tests whether a string contains a specified pattern or not.
Here’s the syntax of the LIKE operator:
expression LIKE pattern ESCAPE escape_characterCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, if the expression matches the pattern, the LIKE operator returns 1. Otherwise, it returns 0.
MySQL provides two wildcard characters for constructing patterns: Percentage % and underscore _ .
- The percentage (
%) wildcard matches any string of zero or more characters. - The underscore (
_) wildcard matches any single character.
For example, s% matches any string starting with the character s such as sun and six. The se_ matches any string starting with se and is followed by any character such as see and sea.
When the pattern contains the wildcard character and you want to treat it as a regular character, you can use the ESCAPE clause.
Typically, you’ll use the LIKE operator in the WHERE clause of the SELECT , DELETE, and UPDATE statement.
MySQL LIKE operator examples
Let’s practice with some examples of using the LIKE operator. We will use the following employees table from the sample database for the demonstration:
1) Using MySQL LIKE operator with the percentage (%) wildcard examples
This example uses the LIKE operator to find employees whose first names start with the letter a:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
firstName LIKE 'a%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)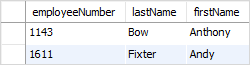
In this example, MySQL scans the whole employees table to find employees whose first names start with the letter a and are followed by any number of characters.
This example uses the LIKE operator to find employees whose last names end with the literal string on e.g., Patterson, Thompson:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
lastName LIKE '%on';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)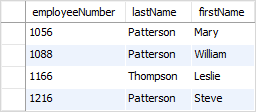
To check if a string contains a substring, you can use the percentage ( % ) wildcard at the beginning and the end of the substring.
For example, the following query uses the LIKE operator to find all employees whose last names contain the substring on:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
lastname LIKE '%on%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)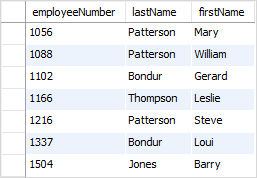
2) Using MySQL LIKE operator with an underscore( _ ) wildcard examples
To find employees whose first names start with the letter T , end with the letter m, and contain any single character between e.g., Tom , Tim, you use the underscore (_) wildcard to construct the pattern as follows:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
firstname LIKE 'T_m';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)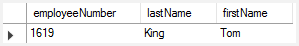
3) Using MySQL NOT LIKE operator example
The MySQL allows you to combine the NOT operator with the LIKE operator to find a string that does not match a specific pattern.
Suppose you want to search for employees whose last names don’t start with the letter B, you can use the NOT LIKE operator as follows:
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
lastName NOT LIKE 'B%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)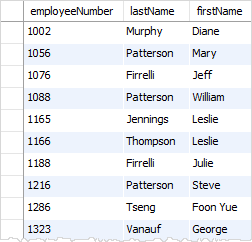
Note that the pattern is not case-sensitive. Therefore, the b% and B% patterns return the same result.
MySQL LIKE operator with the ESCAPE clause
Sometimes the pattern may contain the wildcard characters e.g., 10%, _20, etc.
In this case, you can use the ESCAPE clause to specify the escape character so that the LIKE operator interprets the wildcard character as a literal character.
If you don’t specify the escape character explicitly, the backslash character (\) is the default escape character.
For example, if you want to find products whose product codes contain the string _20 , you can use the pattern %\_20% with the default escape character:
SELECT
productCode,
productName
FROM
products
WHERE
productCode LIKE '%\_20%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Alternatively, you can specify a different escape character e.g., $ using the ESCAPE clause:
SELECT
productCode,
productName
FROM
products
WHERE
productCode LIKE '%$_20%' ESCAPE '$';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)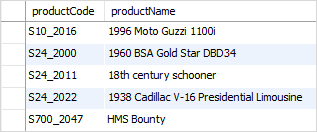
The pattern %$_20% matches any string that contains the _20 string.
Summary
- Use the
LIKEoperator to test if a value matches a pattern. - The
%wildcard matches zero or more characters. - The
_wildcard matches a single character. - Use
ESCAPEclause specifies an escape character other than the default escape character (\). - Use the
NOToperator to negate theLIKEoperator.