Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to rename tables using MySQL RENAME TABLE statement and ALTER TABLE statement.
Introduction to MySQL RENAME TABLE statement
Due to evolving business requirements, you need to rename the existing table to better align with the new situation. MySQL offers a valuable statement for renaming one or more tables.
To rename one or more tables, you can use the RENAME TABLE statement as follows:
RENAME TABLE table_name
TO new_table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
table_name: This is the name of the table that you want to rename.new_table_name: This is the new table name.
The table with the table_name must exist or the RENAME statement will fail with an error.
While executing the RENAME TABLE statement, you need to ensure that there are no active transactions or locked tables.
Note that you cannot use the RENAME TABLE statement to rename a temporary table, but you can use the ALTER TABLE statement to rename a temporary table.
In terms of security, any existing privileges that you granted to the old table must be manually migrated to the new table.
Before renaming a table, it’s important to thoroughly evaluate the potential impact.
For example, you should investigate which applications are currently using the table. Changing the table name would necessitate corresponding changes in the application code that references it.
Additionally, you’ll need to manually adjust other database objects, including views, stored procedures, triggers, and foreign key constraints that reference the table.
We will delve into this in more detail in the following examples.
MySQL RENAME TABLE examples
First, create a new database named hr that includes two tables: employees and departments for the demonstration.
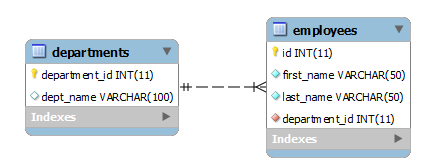
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS hr;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)CREATE TABLE departments (
department_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE employees (
id int AUTO_INCREMENT primary key,
first_name VARCHAR(50) not null,
last_name VARCHAR(50) not null,
department_id INT not null,
FOREIGN KEY (department_id)
REFERENCES departments (department_id)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert sample data into both employees and departments tables:
INSERT INTO departments(dept_name)
VALUES
('Sales'),
('Markting'),
('Finance'),
('Accounting'),
('Warehouses'),
('Production');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)INSERT INTO employees(
first_name, last_name, department_id
)
VALUES
('John', 'Doe', 1),
('Bush', 'Lily', 2),
('David', 'Dave', 3),
('Mary', 'Jane', 4),
('Jonatha', 'Josh', 5),
('Mateo', 'More', 1);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Third, query data from the departments and employees tables:
SELECT
department_id, dept_name
FROM
departments;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)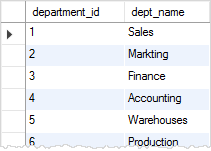
SELECT
id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM
employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)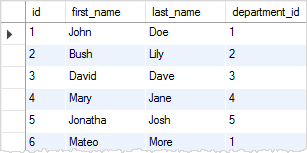
1) Renaming a table referenced by a view
If the table you are going to rename is referenced by a view, the view will become invalid, and you have to adjust the view manually.
For example, we create a view named v_employee_info based on the employees and departments tables as follows:
CREATE VIEW v_employee_info as
SELECT
id,
first_name,
last_name,
dept_name
from
employees
inner join departments USING (department_id);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The views use the inner join clause to join departments and employees tables.
The following SELECT statement returns all data from the v_employee_info view.
SELECT * FROM v_employee_info;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)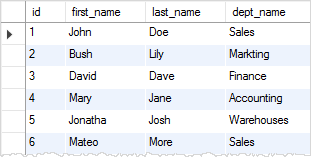
Now we rename the employees to people table and query data from the v_employee_info view again.
RENAME TABLE employees TO people;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)SELECT * FROM v_employee_info;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL returns the following error message:
Error Code: 1356. View 'hr.v_employee_info' references invalid table(s) or
column(s) or function(s) or definer/invoker of view lack rights to use themCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We can use the CHECK TABLE statement to check the status of the v_employee_info view as follows:
CHECK TABLE v_employee_info;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)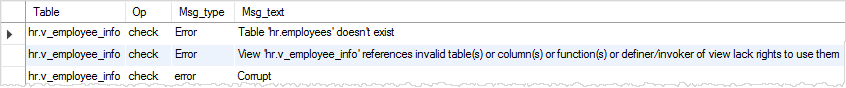
We need to manually change the v_employee_info view so that it refers to the people table instead of the employees table.
2) Renaming a table that is referenced by a stored procedure
In case the table that you are going to rename is referenced by a stored procedure, you have to manually adjust it like you did with the view.
First, rename the people table back to the employees table.
RENAME TABLE people TO employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, create a new stored procedure named get_employee that refers to the employees table.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE get_employee(IN p_id INT)
BEGIN
SELECT first_name, last_name, dept_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments using (department_id)
WHERE id = p_id;
END$$
DELIMITER ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Next, execute the get_employee table to get the data of the employee with ID 1 as follows:
CALL get_employee(1);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)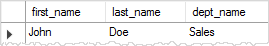
After that, rename the employees to the people table again.
RENAME TABLE employees TO people;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, call the get_employee stored procedure to get the information of the employee with the ID 2:
CALL get_employee(2);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL returns the following error message:
Error Code: 1146. Table 'hr.employees' doesn't existCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To fix this, you need to manually change the employees table in the stored procedure to people table.
3) Renaming a table that is referenced by foreign key constraints
The departments table links to the employees table using the department_id column.
The department_id column in the employees table is the foreign key that references to the departments table.
If you rename the departments table, all the foreign keys that reference the departments table will not be automatically updated. In such cases, you must drop and recreate the foreign keys manually.
RENAME TABLE departments TO depts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We delete a department with id 1, because of the foreign key constraint, all rows in the people table should be also deleted.
However, we renamed the departments table to the depts table without updating the foreign key manually, MySQL returns an error as illustrated below:
DELETE FROM depts
WHERE
department_id = 1Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Error Code: 1451. Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`hr`.`people`, CONSTRAINT `people_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `depts` (`department_id`))Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Renaming multiple tables
We can also use the RENAME TABLE statement to rename multiple tables at a time. See the following statement:
RENAME TABLE
table_name1 TO new_table_name1,
table_name2 TO new_table_name2,
...;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement renames the people and depts tables to employees and departments tables:
RENAME TABLE depts TO departments,
people TO employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note the RENAME TABLE statement is not atomic. It means that if any errors occur, MySQL performs a rollback of all renamed tables to their old names.
Renaming tables using ALTER TABLE statement
You can rename a table using the ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
ALTER TABLE old_table_name
RENAME TO new_table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The ALTER TABLE statement can rename a temporary table while the RENAME TABLE statement cannot.
Renaming temporary table example
First, create a temporary table that contains all unique last names that come from the last_name column of the employees table:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE lastnames
SELECT DISTINCT last_name from employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, use the RENAME TABLE to rename the lastnames table:
RENAME TABLE lastnames TO unique_lastnames;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL returns the following error message:
Error Code: 1017. Can't find file: '.\hr\lastnames.frm' (errno: 2 - No such file or directory)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, use the ALTER TABLE statement to rename the lastnames table.
ALTER TABLE lastnames
RENAME TO unique_lastnames;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Fourth, query data from the unique_lastnames temporary table:
SELECT
last_name
FROM
unique_lastnames;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)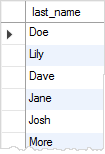
Summary
- Use the
RENAME TABLEorALTER TABLEstatement to rename a table.