Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn various ways to get MySQL row count in the database.
Getting MySQL row count of a single table
To get the row count of a single table, you use the COUNT(*) in a SELECT statement as follows:
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, to get the number of rows in the customers table in the sample database, you use the following statement:
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
customers;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)+----------+
| COUNT(*) |
+----------+
| 122 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Getting MySQL row count of two or more tables
To get the row count of multiple tables, you use the UNION operator to combine result sets returned by each individual SELECT statement.
For example, to get the row count of customers and orders tables in a single query, you use the following statement.
SELECT
'customers' tablename,
COUNT(*) rows
FROM
customers
UNION
SELECT
'orders' tablename,
COUNT(*) rows
FROM
orders;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)+-----------+------+
| tablename | rows |
+-----------+------+
| customers | 122 |
| orders | 326 |
+-----------+------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Getting MySQL row count of all tables in a specific database
To get the row count of all tables in a specific database e.g., classicmodels, you use the following steps:
- First, get all table names in the database
- Second, construct an SQL statement that includes all
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_namestatements for all tables separated byUNION. - Third, execute the SQL statement using a prepared statement.
First, to get all table names of a database, you query from the information_schema database as follows:
SELECT
table_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_schema = 'classicmodels'
AND table_type = 'BASE TABLE';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)+--------------+
| TABLE_NAME |
+--------------+
| customers |
| employees |
| offices |
| orderdetails |
| orders |
| payments |
| productlines |
| products |
+--------------+
8 rows in set (0.02 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Second, to construct the SQL statement, we use the GROUP_CONCAT and CONCAT functions as follows:
SELECT
CONCAT(GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT('SELECT \'',
table_name,
'\' table_name,COUNT(*) rows FROM ',
table_name)
SEPARATOR ' UNION '),
' ORDER BY table_name')
INTO @sql
FROM
table_list;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this query, table_list is a list of table names which is the result of the query in the first step.
The following query uses the first query as a derived table and returns an SQL statement as a string.
SELECT
CONCAT(GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT('SELECT \'',
table_name,
'\' table_name,COUNT(*) rows FROM ',
table_name)
SEPARATOR ' UNION '),
' ORDER BY table_name')
INTO @sql
FROM
(SELECT
table_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_schema = 'classicmodels'
AND table_type = 'BASE TABLE') table_list
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you are using MySQL 8.0+, you can use a MySQL CTE (common table expression) instead of a derived table:
WITH table_list AS (
SELECT
table_name
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'classicmodels' AND
table_type = 'BASE TABLE'
)
SELECT CONCAT(
GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT("SELECT '",table_name,"' table_name,COUNT(*) rows FROM ",table_name) SEPARATOR " UNION "),
' ORDER BY table_name'
)
INTO @sql
FROM table_list;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, you execute the @sql statement using the prepared statement as follows:
PREPARE s FROM @sql;
EXECUTE s;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE s;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)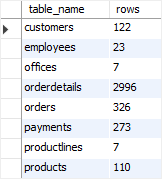
Getting MySQL row count of all tables in a database with one query
A quick way to get the row count of all tables in a database is by querying data from the information_schema database directly:
SELECT
table_name,
table_rows
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_schema = 'classicmodels'
ORDER BY table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)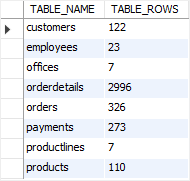
This method is sometimes not accurate because the row count in the information_schema and the actual row count in the tables are not synchronized.
To avoid it, you have to run the ANALYZE TABLE statement before querying the row count from information_schema database.
ANALYZE TABLE table_name, ...;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned various ways to get the row count of one or more tables in the MySQL database.