Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL self join which joins a table to itself using the inner join or left join.
Introduction to MySQL Self Join
A self join allows you to join a table to itself. Since MySQL does not have specific self join syntax, you need to perform a self join via a regular join such as left join or inner join.
Since you reference the same table within a single query, you need to use table aliases to assign the table a temporary name when you reference it for the second time.
To perform a self join, you follow these steps:
- Alias a table: Assign each instance of the table a unique alias to differentiate between them.
- Specify the join condition: Define how the rows from each instance of the table should be compared. In a self join, you typically compare values in columns within the same table.
- Select the desired columns: specify the columns that you want to include in the final result set.
In practice, you use a self join to query hierarchical data such as displaying organization structure or comparing rows within the same table.
MySQL self join examples
We’ll use the employees table from the sample database.

The table employees stores not only employees’ data but also the organization’s data. It uses the reportsto column to determine the manager id of an employee.
1) Performing a self join using an inner join
To obtain the entire organization structure, you can perform a self join on the employees table using the employeeNumber and reportsTo columns:
SELECT
CONCAT(m.lastName, ', ', m.firstName) AS Manager,
CONCAT(e.lastName, ', ', e.firstName) AS 'Direct report'
FROM
employees e
INNER JOIN employees m ON
m.employeeNumber = e.reportsTo
ORDER BY
Manager;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)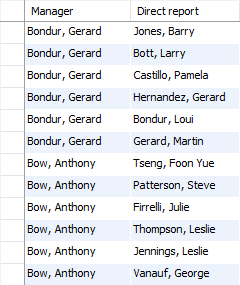
The output displays only the employees who have a manager. However, you don’t see the President because his name is filtered out due to the INNER JOIN clause.
2) Performing a self join using a left join
The President is the employee who does not have any manager or value in the reportsTo column is NULL .
The following statement uses the LEFT JOIN clause instead of INNER JOIN to include the President:
SELECT
IFNULL(CONCAT(m.lastname, ', ', m.firstname),
'Top Manager') AS 'Manager',
CONCAT(e.lastname, ', ', e.firstname) AS 'Direct report'
FROM
employees e
LEFT JOIN employees m ON
m.employeeNumber = e.reportsto
ORDER BY
manager DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)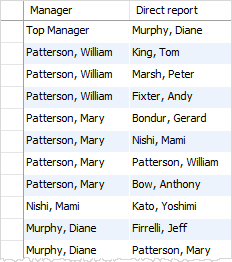
3) Using a self join to compare successive rows within the same table
By using the MySQL self join, you can display a list of customers who are located in the same city by joining the customers table to itself.
SELECT
c1.city,
c1.customerName,
c2.customerName
FROM
customers c1
INNER JOIN customers c2 ON
c1.city = c2.city
AND c1.customername > c2.customerName
ORDER BY
c1.city;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)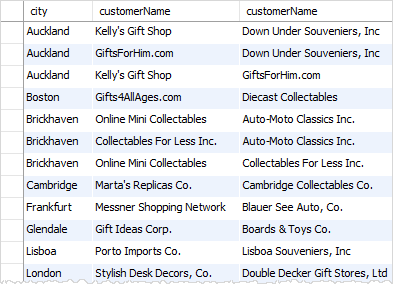
In this example, the table customers is joined to itself using the following join conditions:
c1.city = c2.citymakes sure that both customers have the same city.c1.customerName > c2.customerNameensures that the result does not include the same customer.
Summary
- The MySQL self-join is a technique that joins a table to itself.
- Use table aliases and inner join or left join to perform a self join in MySQL.