Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to select a database in the mysql program and MySQL Workbench by using the USE statement.
Selecting a MySQL database using the mysql client tool
When you log in to a MySQL database server using the mysql client tool without specifying a database name, MySQL server will set the current database to NULL.
First, log in to MySQL using the root user account:
mysql -u root -pCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL will prompt you for a password:
Enter password: Code language: Shell Session (shell)To log in, you need to provide the correct password of the root user account and press Enter. To display the current database, you use the following statement:
SELECT database();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It’ll return the following:
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| NULL |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: Shell Session (shell)It means the current database is not set. If you issue a statement, MySQL will issue an error. For example:
SELECT * FROM t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Error:
ERROR 1046 (3D000): No database selectedCode language: plaintext (plaintext)To select a database to work with, you use the USE statement:
USE database_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statement uses the USE statement to set the current database to classicmodels:
USE classicmodels;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you see the following message, it means that you have changed the database to classicmodels successfully:
Database changedCode language: Shell Session (shell)To verify it, you can use the select database() statement:
SELECT database();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It’ll return something like:
+---------------+
| database() |
+---------------+
| classicmodels |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: Shell Session (shell)If the classicmodels database doesn’t exist, you’ll get the following error after executing the USE statement:
ERROR 1049 (42000): Unknown database 'classicmodels'Code language: Shell Session (shell)In this case, you need to find which databases are available on your server by using the show databases statement:
SHOW DATABASES;The output may look like the following:
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.02 sec)Code language: Shell Session (shell)Selecting a database when you login
If you know which database you want to work with before you log in, you can use the -D flag. For example, the following command connects to the classicmodels database with the user account root:
mysql -u root -D classicmodels -pCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this command, we specify the database classicmodels after the -D flag.
After entering the password and logging in successfully, you can check the current database:
SELECT database();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+---------------+
| database() |
+---------------+
| classicmodels |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: Shell Session (shell)Selecting a database in MySQL Workbench
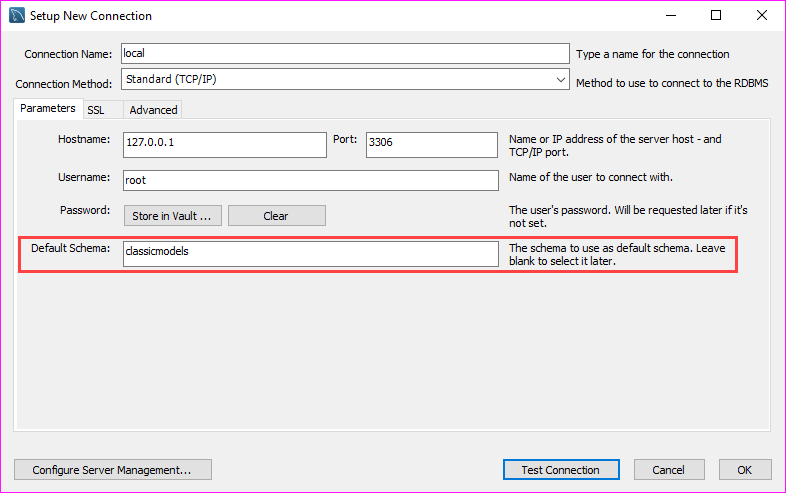
If you connect to a MySQL Server via the MySQL Workbench application, you can select a database when you create the database connection as shown in the following screenshot:
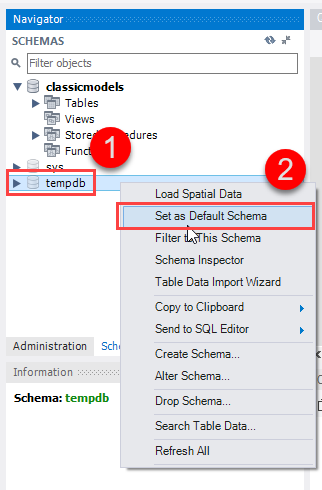
Once logged in, you can select another database by issuing the USE statement or use the Set As Default Schema feature provided by MySQL Workbench:
In this tutorial, you have learned various ways to select a MySQL database via the mysql program and MySQL Workbench application.