Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL GREATEST and LEAST functions to find the greatest and smallest values of two or more fields respectively.
Introduction to MySQL GREATEST and LEAST functions
Both GREATEST and LEAST functions take N arguments and return the greatest and smallest values respectively. The following illustrates the syntax of the GREATEST and LEAST function:
GREATEST(value1, value2, ...);
LEAST(value1,value2,...);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The arguments may have mixed data types. The following comparison rules are applied to both functions:
- If any argument is NULL, both functions return NULLs immediately without doing any comparison.
- If functions are used in the INT or REAL contexts, or all arguments are integer-valued or REAL-valued, they are compared as INT and REAL respectively.
- If arguments consist of both numbers and strings, the functions will compare them as numbers.
- If a least an argument is a non-binary (character) string, the functions will compare the arguments as non-binary strings.
- In all other cases, the functions compare arguments as binary strings.
The following examples demonstrate how the GREATEST and LEAST functions work.
SELECT GREATEST(10, 20, 30), -- 30
LEAST(10, 20, 30); -- 10
SELECT GREATEST(10, null, 30), -- null
LEAST(10, null , 30); -- null
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL GREATEST and LEAST examples
Let’s create a new table for the demonstration.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS revenues (
company_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
q1 DECIMAL(19 , 2 ),
q2 DECIMAL(19 , 2 ),
q3 DECIMAL(19 , 2 ),
q4 DECIMAL(19 , 2 )
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The revenues table consists of company_id as the primary key and four columns to store revenues of the company in each quarter.
The following statement inserts two rows into the revenues table.
INSERT INTO revenues(company_id,q1,q2,q3,q4)
VALUES (1,100,120,110,130),
(2,250,260,300,310);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To get the highest and lowest revenues for each company, you use the GREATEST and LOWEST functions as follows:
SELECT
company_id,
LEAST(q1, q2, q3, q4) low,
GREATEST(q1, q2, q3, q4) high
FROM
revenues;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)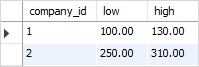
Both GREATEST and LEAST functions return NULLs if any argument is NULL which may not be what you expected.
To avoid this, you can use the IFNULL function to treat NULL as zero to perform the numeric comparison.
The following statement inserts a new row into the revenues table with a NULL value in the q4 column.
INSERT INTO revenues(company_id,q1,q2,q3,q4)
VALUES (3,100,120,110,null);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you use the GREATEST and LEAST functions to query data, you get the result as designed.
SELECT
company_id,
LEAST(q1, q2, q3, q4) low,
GREATEST(q1, q2, q3, q4) high
FROM
revenues;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)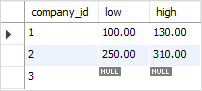
As you can see, the low and high values of the company id 3 are NULLs.
To avoid this, you can use the IFNULL function as follows:
SELECT
company_id,
LEAST(IFNULL(q1, 0),
IFNULL(q2, 0),
IFNULL(q3, 0),
IFNULL(q4, 0)) low,
GREATEST(IFNULL(q1, 0),
IFNULL(q2, 0),
IFNULL(q3, 0),
IFNULL(q4, 0)) high
FROM
revenues;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)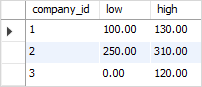
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL GREATEST and LEAST functions to find the greatest and least values in a list of values.