Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function to return the position of a string in a comma-separated list of strings.
Introduction to MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function
MySQL provides a built-in string function called FIND_IN_SET() that allows you to find the position of a string within a comma-separated list of strings.
The following illustrates the syntax of the FIND_IN_SET function:
FIND_IN_SET(needle,haystack);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The FIND_IN_SET function accepts two parameters:
needleis the string that you want to find.haystackis a list of comma-separated strings that are to be searched.
The FIND_IN_SET() function returns an integer or NULL depending on the value of the arguments:
- Return a
NULLvalue if eitherneedleorhaystackisNULL. - Return zero if the
needleis not in thehaystackor thehaystackis an empty string. - Return a positive integer if the
needleis in thehaystack.
Note that the function will not work properly if the needle contains a comma (,). In addition, MySQL will use the bit arithmetic optimization if the needle is a constant string and the haystack is a column of type SET.
The MySQL FIND_IN_SET() examples
Let’s take some examples to understand how the MySQL FIND_IN_SET works.
1) Simple FIND_IN_SET() function examples
The following statement returns 2 because y has the second position in 'x,y,z' string.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('y','x,y,z'); -- 2Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement returns 0 because a is not in the 'x,y,z' list.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('a','x,y,z');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement also returns 0 because the second argument is empty.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('a','');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement returns NULL because the first argument is NULL.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET(NULL,'x,y,z');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement also returns NULL because the second argument is NULL.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('a',NULL);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Using the FIND_IN_SET() function to query data from a table example
First, create a new table named divisions using the following statement.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS divisions (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
belts VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the divisions table.
INSERT INTO divisions(name,belts)
VALUES ('O-1','white,yellow,orange'),
('O-2','purple,green,blue'),
('O-3','brown,red,black'),
('O-4','white,yellow,orange'),
('O-5','purple,green,blue'),
('O-6','brown,red'),
('O-7','black'),
('O-8','white,yellow,orange'),
('O-9','purple,green,blue'),
('O-10','brown,red');
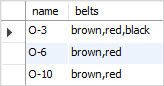
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, find the division that accepts the red belt using the FIND_IN_SET() function:
SELECT
name,
belts
FROM
divisions
WHERE
FIND_IN_SET('red', belts);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Negating FIND_IN_SET() function
The FIND_IN_SET() function returns zero, which is false in MySQL, when the first argument is not found in the second argument. Hence, you can negate the FIND_IN_SET() function using the NOT operator.
The following example uses the NOT operator with the FIND_IN_SET() function to find the divisions that do not accept the black belt:
SELECT
name, belts
FROM
divisions
WHERE
NOT FIND_IN_SET('black', belts);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)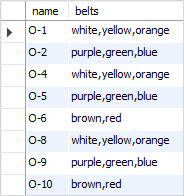
MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function vs. IN operator
The IN operator determines whether a value matches any value in a set. The following example uses the IN operator to find the division whose name is O-1 or O-2:
SELECT
name, belts
FROM
divisions
WHERE
name IN ('O-1' , 'O-2');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)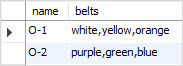
This statement uses the FIND_IN_SET() function and returns the same result as the above query:
SELECT
name,
belts
FROM
divisions
WHERE
FIND_IN_SET(name, 'O-1,O-2');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)So the column IN (x, y, z) expression is the same as FIND_IN_SET(column, 'x,y,z').
The IN operator can take multiple arguments separated by a comma, while the FIND_IN_SET() function can take only two arguments.
In practice, you use the IN operator to match a value against a list of values, you use the FIND_IN_SET() function to match a value with a comma-separated list of values.
Summary
- Use the MySQL
FIND_IN_SET()function to find a string in a comma-separated list of strings.