Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL IF statement to execute a block of SQL code based on a specified condition.
Note that MySQL has an IF() function that differs from the IF statement described in this tutorial.
The IF statement allows you to evaluate one or more conditions and execute the corresponding code block if the condition is true.
The IF statement has three forms:
IF...THENstatement: Evaluate one condition and execute a code block if the condition is true.IF...THEN...ELSEstatement: Evaluate one condition and execute a code block if the condition is true; otherwise, execute another code block.IF...THEN...ELSEIF...ELSEstatement: Evaluate multiple conditions and execute a code block if a condition is true. If all conditions are false, execute the code block in theELSEbranch.
IF-THEN statement
The IF...THEN statement allows you to execute a set of SQL statements based on a specified condition.
The following illustrates the syntax of the IF-THEN statement:
IF condition THEN
statements;
END IF;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, define a condition to execute the code between the
IF...THENandEND IF. If theconditionis true, the statements betweenIF-THENandEND IFwill execute. Otherwise, control is passed to the next statement following theEND IF. - Second, specify the code that will execute if the
conditionevaluates toTRUE.
We’ll use the customers table from the sample database for the demonstration:
The following creates a new stored procedure named GetCustomerLevel() in the sample database:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel(
IN pCustomerNumber INT,
OUT pCustomerLevel VARCHAR(20))
BEGIN
DECLARE credit DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0;
SELECT creditLimit
INTO credit
FROM customers
WHERE customerNumber = pCustomerNumber;
IF credit > 50000 THEN
SET pCustomerLevel = 'PLATINUM';
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The stored procedure GetCustomerLevel() accepts two parameters: pCustomerNumber and pCustomerLevel.
- First, select
creditLimitof the customer specified by thepCustomerNumberfrom thecustomerstable and store it in the local variablecredit. - Then, set the value for the
OUTparameterpCustomerLeveltoPLATINUMif the credit limit of the customer is greater than50,000.
This statement finds all customers that have a credit limit greater than 50,000:
SELECT
customerNumber,
creditLimit
FROM
customers
WHERE
creditLimit > 50000
ORDER BY
creditLimit DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
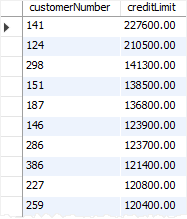
These statements call the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure for customer 141 and show the value of the OUT parameter pCustomerLevel:
CALL GetCustomerLevel(141, @level);
SELECT @level;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+----------+
| @level |
+----------+
| PLATINUM |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Because the customer 141 has a credit limit greater than 50,000, its level is set to PLATINUM as expected.
IF-THEN-ELSE statement
In case you want to execute other statements when the condition in the IF branch does not evaluate to TRUE, you can use the IF-THEN-ELSE statement as follows:
IF condition THEN
statements;
ELSE
else-statements;
END IF;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, if the condition evaluates to true, the statements between IF-THEN and ELSE execute. Otherwise, the else-statements between the ELSE and END IF execute.
Let’s modify the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure.
First, drop the GetCustomerLevel stored procedure:
DROP PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, create the GetCustomerLevel stored procedure with the new code:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel(
IN pCustomerNumber INT,
OUT pCustomerLevel VARCHAR(20))
BEGIN
DECLARE credit DECIMAL DEFAULT 0;
SELECT creditLimit
INTO credit
FROM customers
WHERE customerNumber = pCustomerNumber;
IF credit > 50000 THEN
SET pCustomerLevel = 'PLATINUM';
ELSE
SET pCustomerLevel = 'NOT PLATINUM';
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In the updated stored procedure, we include the ELSE branch. If the credit is not greater than 50,000, we set the customer level to NOT PLATINUM in the block between ELSE and END IF.
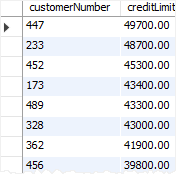
This query finds customers that have credit limits less than or equal 50,000:
SELECT
customerNumber,
creditLimit
FROM
customers
WHERE
creditLimit <= 50000
ORDER BY
creditLimit DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This picture shows the partial output:
The following statements call the stored procedure for customer number 447 and show the value of the OUT parameter pCustomerLevel:
CALL GetCustomerLevel(447, @level);
SELECT @level;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+--------------+
| @level |
+--------------+
| NOT PLATINUM |
+--------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The credit limit of the customer 447 is less than 50,000, therefore, the statement in the ELSE branch executes and sets the value of the OUT parameter pCustomerLevel to NOT PLATINUM.
IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement
The IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement allows you to check multiple conditions sequentially. Here’s the basic syntax of the IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement:
IF condition THEN
statements;
ELSEIF elseif-condition THEN
statements;
...
ELSE
statements;
END IF;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- If the initial condition is true, its associated statements are executed. If it’s false, the program checks the next condition (
ELSEIF). - If any of the
ELSEIFconditions are true, the corresponding statements are executed. - If none of the conditions is true, the statements in the
ELSEblock are executed.
We will modify the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure to use the IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement.
First, drop the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure:
DROP PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, recreate the new GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure that uses the IF-THEN-ELSEIF-ELSE statement.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel(
IN pCustomerNumber INT,
OUT pCustomerLevel VARCHAR(20))
BEGIN
DECLARE credit DECIMAL DEFAULT 0;
SELECT creditLimit
INTO credit
FROM customers
WHERE customerNumber = pCustomerNumber;
IF credit > 50000 THEN
SET pCustomerLevel = 'PLATINUM';
ELSEIF credit <= 50000 AND credit > 10000 THEN
SET pCustomerLevel = 'GOLD';
ELSE
SET pCustomerLevel = 'SILVER';
END IF;
END $$
DELIMITER ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this stored procedure:
- If the credit is greater than
50,000, the level of the customer isPLATINUM. - If the credit is less than or equal
50,000and greater than10,000, then the level of customer isGOLD. - Otherwise, the level of the customer is
SILVER.
These statements call the stored procedure GetCustomerLevel() and show the level of the customer 447:
CALL GetCustomerLevel(447, @level);
SELECT @level;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+--------+
| @level |
+--------+
| GOLD |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Summary
- Use
IF...THENstatement to conditionally execute a block of statements based on the evaluation of a specified condition. - Use
IF...THEN...ELSEstatement to execute a block of statements if a specified condition is true and an alternative block of statements if the condition is false. - Use
IF...THEN...ELSEIF...ELSEstatement to evaluate multiple conditions sequentially and execute corresponding blocks of statements based on the first true condition, with an optional block of statements to execute if none of the conditions is true.