Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL REPEAT statement to execute one or more statements until a condition is true.
Introduction to the MySQL REPEAT statement
The REPEAT statement creates a loop that repeatedly executes a block of statements until a condition is true.
Here is the basic syntax of the REPEAT statement:
[begin_label:] REPEAT
statement;
UNTIL condition
END REPEAT [end_label]
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The REPEAT repeatedly executes the statements inside its block until the specified condition becomes true.
It’s important to note that the REPEAT checks the condition after the execution of the block, meaning that the block always executes at least once.
The REPEAT statement can have optional labels before the REPEAT keyword and after the END REPEAT keyword.
The following flowchart illustrates how the REPEAT statement works:
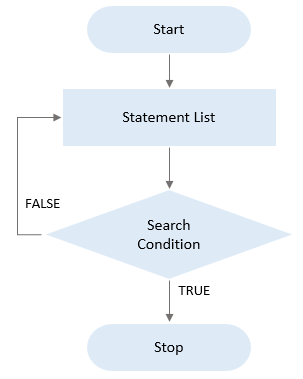
MySQL REPEAT statement example
This statement creates a stored procedure called RepeatDemo that uses the REPEAT statement to concatenate numbers from 1 to 9:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE RepeatDemo()
BEGIN
DECLARE counter INT DEFAULT 1;
DECLARE result VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT '';
REPEAT
SET result = CONCAT(result,counter,',');
SET counter = counter + 1;
UNTIL counter >= 10
END REPEAT;
-- display result
SELECT result;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this stored procedure:
First, declare two variables counter and result and set their initial values to 1 and blank.
The counter variable is used for counting from 1 to 9 in the loop. And the result variable is used for storing the concatenated string after each loop iteration.
Second, append counter value to the result variable using the CONCAT() function until the counter is greater than or equal to 10.
The following statement calls the RepeatDemo() stored procedure:
CALL RepeatDemo();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
+--------------------+
| result |
+--------------------+
| 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, |
+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary
- Use the MySQL
REPEATstatement to execute one or more statements until a condition is true.