Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn various ways to delete duplicate rows in MySQL.
In the previous tutorial, we have shown you how to find duplicate values in a table. Once the duplicate rows are identified, you may want to delete them to clean up your data.
Prepare sample data
The following script creates table contacts and inserts sample data into the contacts table for the demonstration.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS contacts;
CREATE TABLE contacts (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO contacts (first_name,last_name,email)
VALUES ('Carine ','Schmitt','[email protected]'),
('Jean','King','[email protected]'),
('Peter','Ferguson','[email protected]'),
('Janine ','Labrune','[email protected]'),
('Jonas ','Bergulfsen','[email protected]'),
('Janine ','Labrune','[email protected]'),
('Susan','Nelson','[email protected]'),
('Zbyszek ','Piestrzeniewicz','[email protected]'),
('Roland','Keitel','[email protected]'),
('Julie','Murphy','[email protected]'),
('Kwai','Lee','[email protected]'),
('Jean','King','[email protected]'),
('Susan','Nelson','[email protected]'),
('Roland','Keitel','[email protected]');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you can execute this script to recreate test data after you execute a DELETE statement.
This query returns data from the contacts table:
SELECT * FROM contacts
ORDER BY email;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)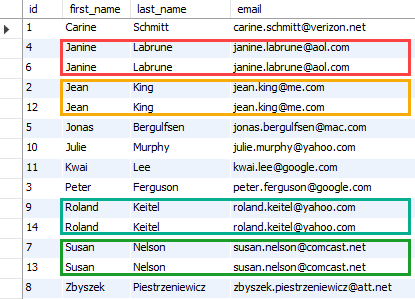
The following query returns the duplicate emails in the contacts table:
SELECT
email, COUNT(email)
FROM
contacts
GROUP BY
email
HAVING
COUNT(email) > 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)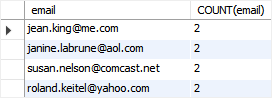
As you can see, we have four rows with duplicate emails.
1) Delete duplicate rows using the DELETE JOIN statement
MySQL provides you with the DELETE JOIN statement that allows you to remove duplicate rows quickly.
The following statement deletes duplicate rows and keeps the highest id:
DELETE t1 FROM contacts t1
INNER JOIN contacts t2
WHERE
t1.id < t2.id AND
t1.email = t2.email;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.10 sec)Code language: CSS (css)Because we reference the contacts table twice, we need to use the table aliases t1 and t2.
The output indicates that four rows were deleted. You can execute the query that finds duplicate emails again to verify the delete:
SELECT
email,
COUNT(email)
FROM
contacts
GROUP BY
email
HAVING
COUNT(email) > 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Empty set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The query returns an empty set, which means that the duplicate rows have been deleted.
Let’s verify the data from the contacts table:
SELECT * FROM contacts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)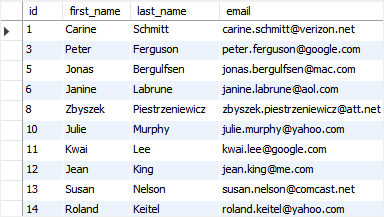
The rows with id 2, 4, 7, and 9 have been deleted.
In case you want to delete duplicate rows and keep the lowest id, you can use the following statement:
DELETE c1 FROM contacts c1
INNER JOIN contacts c2
WHERE
c1.id > c2.id AND
c1.email = c2.email;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you can execute the script for creating contacts table again and test this query. The following output shows the data of the contacts table after removing duplicate rows.
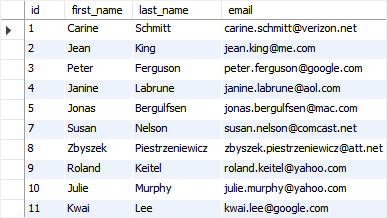
2) Delete duplicate rows using an intermediate table
The following shows the steps for removing duplicate rows using an intermediate table:
- Create a new table with the structure the same as the original table that you want to delete duplicate rows.
- Insert distinct rows from the original table to the immediate table.
- Drop the original table and rename the immediate table to the original table.
The following queries illustrate the steps:
Step 1. Create a new table whose structure is the same as the original table:
CREATE TABLE source_copy LIKE source;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Step 2. Insert distinct rows from the original table to the new table:
INSERT INTO source_copy
SELECT * FROM source
GROUP BY col; -- column that has duplicate valuesCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Step 3. Drop the original table and rename the immediate table to the original one
DROP TABLE source;
ALTER TABLE source_copy RENAME TO source;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statements delete rows with duplicate emails from the contacts table:
-- step 1
CREATE TABLE contacts_temp
LIKE contacts;
-- step 2
INSERT INTO contacts_temp
SELECT *
FROM contacts
GROUP BY email;
-- step 3
DROP TABLE contacts;
ALTER TABLE contacts_temp
RENAME TO contacts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)3) Delete duplicate rows using the ROW_NUMBER() function
Note that MySQL supports the ROW_NUMBER() function starting from version 8.02 so you should check your MySQL version before using the function.
The following statement uses the ROW_NUMBER() function to assign a sequential integer number to each row. If the email is duplicate, the row number will be greater than one.
SELECT
id,
email,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
PARTITION BY email
ORDER BY
email
) AS row_num
FROM
contacts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement returns id list of the duplicate rows:
SELECT
id
FROM
(
SELECT
id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
PARTITION BY email
ORDER BY
email
) AS row_num
FROM
contacts
) t
WHERE
row_num > 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)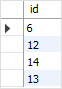
You need to delete the duplicate rows from the contacts table using the DELETE statement with a subquery in the WHERE clause:
DELETE FROM
contacts
WHERE
id IN (
SELECT
id
FROM
(
SELECT
id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
PARTITION BY email
ORDER BY
email
) AS row_num
FROM
contacts
) t
WHERE
row_num > 1
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL issued the following message:
4 row(s) affectedIn this tutorial, you have learned how to delete duplicate rows in MySQL.