Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the MySQL DENSE_RANK() function and how to apply it to find the rank of rows in a partition or result set.
Introduction to MySQL DENSE_RANK function
The DENSE_RANK() is a window function that assigns a rank to each row within a partition or result set with no gaps in ranking values.
The rank of a row is increased by one from the number of distinct rank values that come before the row.
Here’s the basic syntax of the DENSE_RANK() function:
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY partition_expression
ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC|DESC]
)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divides the result sets produced by theFROMclause into partitions. TheDENSE_RANK()function is applied to each partition independently. - Second, the
ORDER BYclause specifies the order of rows in each partition on which theDENSE_RANK()function operates.
If a partition has two or more rows with the same rank value, each of these rows will be assigned the same rank.
Unlike the RANK() function, the DENSE_RANK() function always returns consecutive rank values.
Suppose you have a table t with some sample data as follows:
CREATE TABLE t (
val INT
);
INSERT INTO t(val)
VALUES(1),(2),(2),(3),(4),(4),(5);
SELECT * FROM t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
+------+
| val |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following statement uses the DENSE_RANK() function to assign a rank to each row:
SELECT
val,
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
ORDER BY val
) my_rank
FROM t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
+------+---------+
| val | my_rank |
+------+---------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
+------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)MySQL DENSE_RANK() function example
We will use the following sales table for the demonstration:
CREATE TABLE sales(
sales_employee VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
fiscal_year INT NOT NULL,
sale DECIMAL(14,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(sales_employee,fiscal_year)
);
INSERT INTO sales(sales_employee,fiscal_year,sale)
VALUES('Bob',2016,100),
('Bob',2017,150),
('Bob',2018,200),
('Alice',2016,150),
('Alice',2017,100),
('Alice',2018,200),
('John',2016,200),
('John',2017,150),
('John',2018,250);
SELECT * FROM sales;Code language: PHP (php)Output:
+----------------+-------------+--------+
| sales_employee | fiscal_year | sale |
+----------------+-------------+--------+
| Alice | 2016 | 150.00 |
| Alice | 2017 | 100.00 |
| Alice | 2018 | 200.00 |
| Bob | 2016 | 100.00 |
| Bob | 2017 | 150.00 |
| Bob | 2018 | 200.00 |
| John | 2016 | 200.00 |
| John | 2017 | 150.00 |
| John | 2018 | 250.00 |
+----------------+-------------+--------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following statement uses the DENSE_RANK() function to rank the sales employees by sale amount.
SELECT
sales_employee,
fiscal_year,
sale,
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY fiscal_year
ORDER BY sale DESC
) sales_rank
FROM
sales;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is as follows:
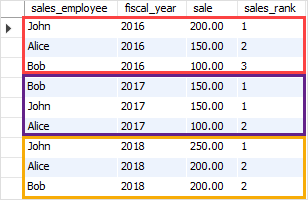
In this example:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divided the result sets into partitions using fiscal year. - Second, the
ORDER BYclause specified the order of the sales employees by sales in descending order. - Third, the
DENSE_RANK()function is applied to each partition with the order of the rows specified by theORDER BYclause.
Summary
- Use the MySQL
DENSE_RANK()function to rank rows in each partition of a result set.