Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL FIRST_VALUE() function to get the first row of a frame, partition, or result set.
Introduction to MySQL FIRST_VALUE() function
The FIRST_VALUE() is a window function that allows you to select the first row of a window frame, partition, or result set.
The following illustrates the syntax of the FIRST_VALUE() function:
FIRST_VALUE (expression) OVER (
[partition_clause]
[order_clause]
[frame_clause]
)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
expression
The FIRST_VALUE() function returns the value of the expression from the first row of the window frame.
The OVER clause consists of three clauses: partition_clause, order_clause, and frame_clause.
partition_clause
The partition_clause clause divides the rows of the result sets into partitions to which the function applies independently. The partition_clause has the following syntax:
PARTITION BY expr1, expr2, ...Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)order_clause
The order_clause clause specifies the logical order of rows in each partition on which the FIRST_VALUE() function operates. The following shows the syntax of the order_clause:
ORDER BY expr1 [ASC|DESC], expr2 [ASC|DESC], ...Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)frame_clause
The frame_clause defines the subset (or frame) of the current partition. For detailed information on the frame clause syntax, check out the window functions tutorial.
MySQL FIRST_VALUE() function examples
The following statements create a new table named overtime and insert sample data for the demonstration:
CREATE TABLE overtime (
employee_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
hours INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (employee_name , department)
);
INSERT INTO overtime(employee_name, department, hours)
VALUES('Diane Murphy','Accounting',37),
('Mary Patterson','Accounting',74),
('Jeff Firrelli','Accounting',40),
('William Patterson','Finance',58),
('Gerard Bondur','Finance',47),
('Anthony Bow','Finance',66),
('Leslie Jennings','IT',90),
('Leslie Thompson','IT',88),
('Julie Firrelli','Sales',81),
('Steve Patterson','Sales',29),
('Foon Yue Tseng','Sales',65),
('George Vanauf','Marketing',89),
('Loui Bondur','Marketing',49),
('Gerard Hernandez','Marketing',66),
('Pamela Castillo','SCM',96),
('Larry Bott','SCM',100),
('Barry Jones','SCM',65);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)1) Using MySQL FIRST_VALUE() function over the whole query result set example
The following statement gets the employee’s name, overtime, and the employee who has the least overtime:
SELECT
employee_name,
hours,
FIRST_VALUE(employee_name) OVER (
ORDER BY hours
) least_over_time
FROM
overtime;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
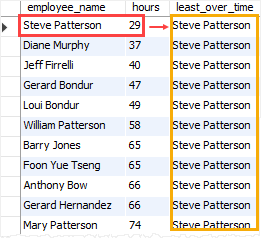
In this example, the ORDER BY clause ordered the rows in the result set by hours and the FIRST_VALUE() picked the first row indicating the employee who had the least overtime.
2) Using MySQL FIRST_VALUE() function with partitions example
The following statement finds the employee who has the least overtime in every department:
SELECT
employee_name,
department,
hours,
FIRST_VALUE(employee_name) OVER (
PARTITION BY department
ORDER BY hours
) least_over_time
FROM
overtime;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is:
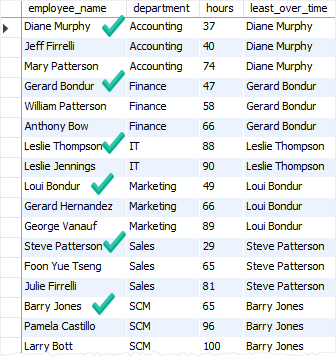
In this example:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divides the employees into partitions by departments. In other words, each partition consists of employees who belong to the same department. - Second, the
ORDER BYclause specifies the order of rows in each partition. - Third, the
FIRST_VALUE()operates on each partition sorted by the hours. It returns the first row in each partition which is the employee who has the least overtime within the department.
Summary
- Use the MySQL
FIRST_VALUE()function to get the first row of a window frame.